A Standards-Aligned 11-Week Unit Plan With Multiplication and Division Worksheets, Lesson Plan and Printables for Grade 3
Target important math skills with this comprehensive unit plan designed for Common Core Math Standards for Grade 3. Including helpful teaching notes for 11 weeks of lessons, accompanying games and activities, ready-to-use assessments and word problems for multiplication and division, this no-prep, hassle-free unit plan has everything you need for teaching multiplication and division to your Grade 3 class!What's Included in this Unit Plan
For the teacher:- Fully-resourced 11 week unit plan aligned with Common Core Math Standards for Grade 3
- Printable worksheets, activities and problems to supplement lessons throughout the multiplication and division unit
- Teaching notes with instructions, ideas for differentiation and strategies to target key math skills
- Multiplication games, multiplication and division word problems, and a huge variety of fun activities including both individual and group tasks
- Ready-to-use multiplication and division assessment sheets to monitor and track student progress plus timed ‘challenge’ assessment sheets
- Handy tools, grids, templates and printables to help students master multiplication and division facts
Standards Alignment:
This Multiplication and Division Unit Plan targets the following Common Core Math Standards for Grade 3.
Represent and solve problems involving multiplication and division- CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.3.OA.A.1 - Interpret products of whole numbers, e.g., interpret 5 × 7 as the total number of objects in 5 groups of 7 objects each. For example, describe a context in which a total number of objects can be expressed as 5 × 7.
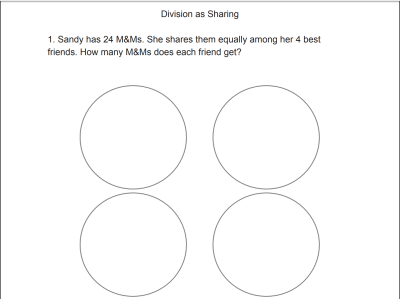
- CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.3.OA.A.2 - Interpret whole-number quotients of whole numbers, e.g., interpret 56 ÷ 8 as the number of objects in each share when 56 objects are partitioned equally into 8 shares, or as a number of shares when 56 objects are partitioned into equal shares of 8 objects each. For example, describe a context in which a number of shares or a number of groups can be expressed as 56 ÷ 8.
- CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.3.OA.A.3 - Use multiplication and division within 100 to solve word problems in situations involving equal groups, arrays, and measurement quantities, e.g., by using drawings and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem.
- CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.3.OA.A.4 - Determine the unknown whole number in a multiplication or division equation relating three whole numbers. For example, determine the unknown number that makes the equation true in each of the equations 8 × ? = 48, 5 = _ ÷ 3, 6 × 6 = ?
- CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.3.OA.B.5 - Apply properties of operations as strategies to multiply and divide. Examples: If 6 × 4 = 24 is known, then 4 × 6 = 24 is also known. (Commutative property of multiplication.) 3 × 5 × 2 can be found by 3 × 5 = 15, then 15 × 2 = 30, or by 5 × 2 = 10, then 3 × 10 = 30. (Associative property of multiplication.) Knowing that 8 × 5 = 40 and 8 × 2 = 16, one can find 8 × 7 as 8 × (5 + 2) = (8 × 5) + (8 × 2) = 40 + 16 = 56. (Distributive property.)
- CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.3.OA.B.6 - Understand division as an unknown-factor problem. For example, find 32 ÷ 8 by finding the number that makes 32 when multiplied by 8.
- CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.3.OA.C.7 - Fluently multiply and divide within 100, using strategies such as the relationship between multiplication and division (e.g., knowing that 8 × 5 = 40, one knows 40 ÷ 5 = 8) or properties of operations. By the end of Grade 3, know from memory all products of two one-digit numbers. Solve problems involving the four operations, and identify and explain patterns in arithmetic.
- CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.3.OA.D.8 - Solve two-step word problems using the four operations. Represent these problems using equations with a letter standing for the unknown quantity. Assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies including rounding.
- CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.3.OA.D.9 - Identify arithmetic patterns (including patterns in the addition table or multiplication table), and explain them using properties of operations. For example, observe that 4 times a number is always even, and explain why 4 times a number can be decomposed into two equal addends.
- CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.3.NBT.A.3 - Multiply one-digit whole numbers by multiples of 10 in the range 10-90 (e.g., 9 × 80, 5 × 60) using strategies based on place value and properties of operations.